For lightweight project development, teams often use Express.js as the backend because it’s simple enough, easy to get started with, and naturally suitable for RESTful APIs. During usage, I’ve gradually deepened my understanding of Express and found that the official documentation has very little explanation about next, so I’ll organize this to deepen understanding.
The Role of Next
next is responsible for passing control to the next middleware function.
Next Usage Scenarios and Why We Need Next
When handling route requests, we might need the next middleware to process, so we should use the next function. For example, exception handling or branched request processing.
Code Examples
Example 1
router.get("/hello", function (req, res, next) {
res.write("hello");
next();
});
router.get("/hello", function (req, res) {
res.write(" world");
res.end();
});
After execution, result screenshot
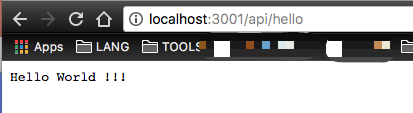
Example 2
router.get("/hello", function (req, res, next) {
if (req.query.name) {
return res.json("hello");
}
else {
next(new Error("No name provided"));
}
});
router.use(function (err, req, res, next) {
res.json({
message: err.message,
error: {}
});
});
Execute request http://localhost:3001/api/hello
Result screenshot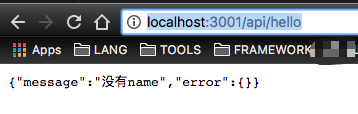
Exception handling is actually one use case of next.
Note: Since exception handling is done after the route request here, the exception middleware handling comes after the route request handling.

