I recently used WebSocket in a project but didn’t know much about it. I spent some time reading “WebSocket”. Here are some takeaways.

The Mission of WebSocket
New technologies solve specific problems—Promises solve callback hell; XHR enables async requests. WebSocket arrived with HTML5 to provide full-duplex communication between the web and backend. Before WS, we relied on polling, and only the client could initiate requests.
With WebSocket, both sides can push messages to each other—that’s its mission.
TLS, SSL, HTTPS
Security matters. For WebSocket, you’ll see WS vs WSS; under HTTPS, use WSS. What are TLS, SSL, and HTTPS?
- TLS (Transport Layer Security) and its predecessor SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) are security protocols that provide confidentiality and integrity.
- HTTPS is HTTP over TLS/SSL, providing encrypted transport and authentication.
- HTTPS is also known as HTTP over TLS.
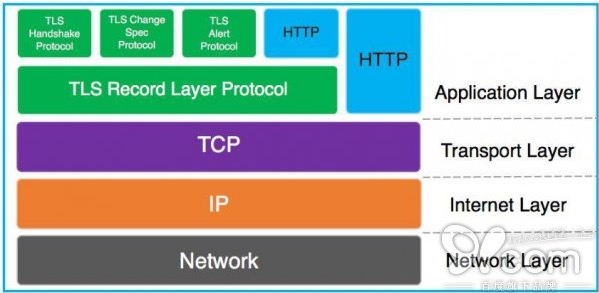
WebSocket, SockJS, STOMP
- WebSocket is a browser/server full-duplex communication technology (application layer) built on TCP that reuses the HTTP handshake.
- WebSocket is an application-layer transport protocol that enables full-duplex comms over a single TCP connection.
- SockJS is a browser JavaScript library that provides a consistent, cross-browser API, falling back when WebSocket isn’t available (e.g., to polling). Spring supports SockJS.
- STOMP is a messaging protocol; since WebSocket doesn’t define message format, STOMP standardizes it.
My stack is React + Spring Boot, so I use WebSocket + SockJS + STOMP.
OSI Seven-Layer Model
Open System Interconnection Model.
I remembered it from college (Xie Xiren’s “Computer Networks”). A quick refresher when I saw “application layer” again.
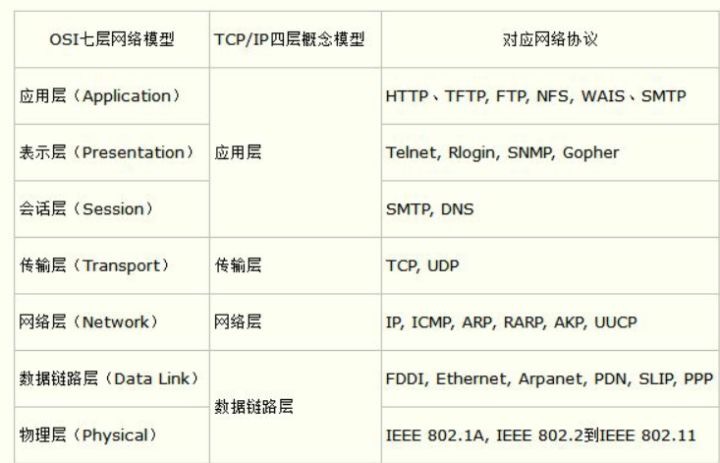
Notes
- The OSI seven-layer model is conceptual.
- In practice, we often use 5 layers (presentation/session are collapsed/omitted).
Where WebSocket Meets HTTP
From connection, subscription, sending/receiving messages, to disconnecting—HTTP is still involved.

- The connection starts as an HTTP GET request.
- Then the WebSocket connection is established (status 101) and full-duplex comms happen there.
- A single logical session involves two requests: one HTTP, one WebSocket.
Useful Status Code
We all know the five HTTP status code classes, but 1xx is rare in RESTful work. You’ll see it here.
101
HTTP 101 Switching Protocol indicates the server is switching protocols as requested via the Upgrade header. The response includes an Upgrade header indicating the target protocol.
HTTP 0.9 — The Web Is Born
Some history:
- HTTP 0.9 was proposed in 1991. Same year as my birth—easy to remember.
- 0.9 supported only GET; POST/PUT arrived in 1.0.
- Today 1.1 is mainstream. HTTP/2 adds multiplexing; many sites enable it (mine too).
- HTTP/3 is coming, using QUIC over UDP instead of TCP. Adoption will be slower since it changes the transport layer.

Final Thoughts
- My understanding is still shallow; learning continues through practice.
- The book is thorough and covers the fundamentals well.
- Reading fills knowledge gaps and is a way to “talk” with experts at a distance.

