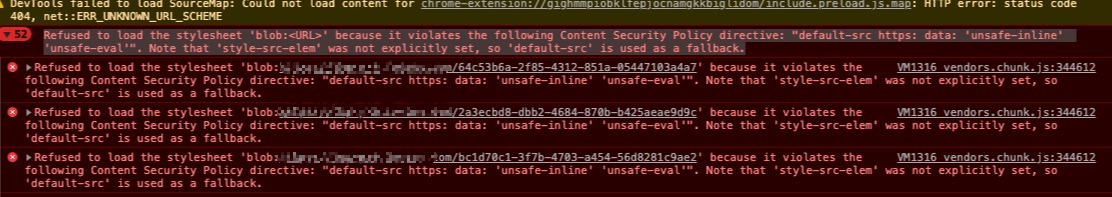
Recently, the project was undergoing security scanning, and the security team reported an issue - CSP was not satisfied. As shown in the image below, the error message was already clear, but since I hadn’t studied this before, I began investigating and learning.
Content Security Policy (CSP)
The essence of CSP is a whitelist system. Developers explicitly tell the client which external resources can be loaded and executed, equivalent to providing a whitelist. Its implementation and execution are all handled by the browser; developers only need to provide the configuration.

Configuration Methods
- Response header configuration
(the method my current project chose) - HTML meta tag configuration
Configuration Control Content
- script-src
- style-src
- img-src
- frame-src
- default-src
- etc.
As mentioned earlier, configuration policies can strictly control our resource types, source addresses, and protocol types.
Posting My Current Configuration
My current configuration is still relatively loose, only controlling that resource sources must be from myself
content-security-policy: "default-src 'self' wss: 'unsafe-inline' file: data: blob: https://*;"

Content Format
How to configure? Just know the format and values.
- script-src, default-src we can call directives, so we configure one or more directives. As above, I only configured
default-src,directives are separated by semicolons - Multiple sources in a single directive, sources can be domains, IPs, protocols. Note that protocols need to include the colon
- unsafe-inline, unsafe-eval, none must have single quotes.
This is why various writing styles exist in directive configuration - semicolons, single quotes, colons, spaces.
Common Security Strategies
- HTTPS - essentially today many websites are
HTTPS. If not, for example, Chrome will indicate the site is insecure. Why is HTTPS secure? Because it encrypts all content. - For high-traffic sites, to improve access speed, we generally CDN-ize static resources like images. But what if these CDN resources get used by others? That would be traffic theft. So there are security strategies, like judging based on
referersource address. If the CDN resource wasn’t requested by site A, then directly intercept. - For example, sessionId, tokens, set as
HttpOnly. Because this information itself doesn’t represent anything - we often use tokens to exchange for user information, so the consumer is the server side. To ensure they won’t be tampered with by scripts, etc., they need to be set. When JavaScript gets cookies, it will skip cookie records with HttpOnly = true.

