I practiced several common algorithm problems today, so I’m marking them down here.
Array Deduplication
reduce
function uniqueArr(arr) {
return arr.reduce((result, item) => {
if (result.includes(item)) {
return result;
}
result.push(item);
return result;
}, []);
}
Set Properties
function uniqueArr(arr) {
return Array.from(new Set(arr));
}
for loop
function uniqueArr(arr) {
const result = [];
arr.forEach((item) => {
if (!result.includes(item)) {
result.push(item);
}
});
return result;
}
Bubble Sort
function bubbleSort(arr) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[j - 1]) {
const temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
arr[j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
Finding Prime Numbers in 1000 Numbers
Notes
- If a number can only be divided by 1 and itself, it’s a prime number
- 1 is not a prime number
The first method should have the highest overhead, as each number needs to calculate from 2 to n-1.
Basic Method
function isPrimeNumber(num) {
if (num === 1 || num === 2) {
return true;
}
for (let index = 2; index < num - 1; index++) {
if (num % index === 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
function getPrimeNumbers(end) {
const result = [];
for (let index = 2; index <= end; index++) {
isPrimeNumber(index) && result.push(index);
}
return result;
}
console.time('prime numbers - method #1');
console.log(getPrimeNumbers(1000));
console.timeEnd('prime numbers - method #1
Trial Division - Improved Version
Note that Math.sqrt square root operation is less efficient than multiplication.
function isPrimeNumber(num) {
if (num === 2) {
return true;
}
for (let index = 2; index * index <= num; index++) {
if (num % index === 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
Regex Method - Clever Approach - Not Recommended
High memory consumption, for understanding only.
function isPrimeNumber3(index) {
return !Boolean(
Array(index)
.fill(1)
.join('')
.match(/^1?$|^(11+?)\1+$/)
);
}
function getPrimeNumbers3(end) {
const result = [];
for (let index = 2; index <= end; index++) {
isPrimeNumber3(index) && result.push(index);
}
return result;
}
Sieve of Eratosthenes
function getPrimeNumbers4(end) {
const result = [];
const defaultPrimes = Array(end + 1).fill(true);
for (let i = 2; i < defaultPrimes.length; i++) {
if (defaultPrimes[i]) {
result.push(i);
for (let j = i * 2; j < defaultPrimes.length; j += i) {
defaultPrimes[j] = false;
}
}
}
return result;
}
Algorithm Performance Comparison
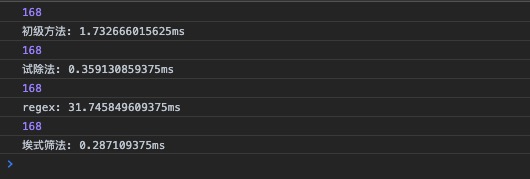
Online Code
I’ve hosted the algorithm on codesandbox, click to view
Final Thoughts
I haven’t paid much attention to algorithms before, but after some deep reflection, I’ve decided to practice deliberately. In fact, algorithms are everywhere - some are abstracted away by various libraries and tools, while others are avoided due to insufficient understanding, which results in increased program overhead. Therefore, I need to strengthen my fundamentals and get started.

