More notes from frontend interview discussions to reinforce basics.
MVVM
MVVM is an architectural pattern. For context, compare common patterns:
MVC
Model–view–controller
- Model — implements domain logic and data management.
- View — UI and its presentation.
- Controller — routes requests and handles input.
MVP
Model–view–presenter
In MVC, Model and View may interact. In MVP, the Presenter mediates between Model and View, typically via interfaces.
MVVM
Model–view–viewmodel
- Model — domain model or data access layer.
- View — the UI users see (structure, layout, appearance).
- ViewModel — an abstraction of the view exposing properties and commands. Instead of a Controller/Presenter, MVVM commonly relies on binding between View and ViewModel.
Notes
- React is not MVVM; it’s essentially ui = render(data).
- Vue isn’t strictly MVVM but borrows many ideas.
- Angular is MVC.
How browsers work
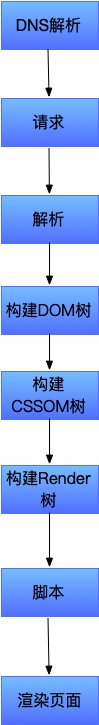
Notes
- Persistent connections: TCP isn’t closed after one HTTP request unless
Connection: close. - One TCP connection can carry multiple HTTP requests.
- With HTTP/2, multiple requests can run in parallel over one TCP connection.
- TCP connections may be kept alive; a refresh may not renegotiate TLS.
- Browsers limit concurrent TCP connections per host (e.g., Chrome ~6).
React Fiber
React Fiber是对核心算法的一次重新实现
From v16, Fiber is the new reconciler. The goal is smoother updates under heavy UI by slicing work into chunks and yielding back to the browser between units to avoid blocking rendering.
Diagrams below highlight differences between v15 and v16 with Fiber:

How Redux updates components
Essentially, the connect HOC subscribes components to the store; on changes, Redux triggers updates (e.g., via component.forceUpdate under the hood).