I’ve been developing extensions recently and encountered some pitfalls. Here’s a summary of what I’ve learned.
Programmatic Popup Opening?
Popup does not support programmatic opening. A workaround solution is to create a new window and open popup.html.
chrome.windows.create({
url: `popup.html`,
type: 'popup',
height: 640,
width: 357,
left: 100,
top: 100,
focused: true,
})
Disable Window Resize
const size = [document.body.clientWidth, document.body.clientHeight];
/**
* Prevent popup window resizing. When creating a new window, resizing cannot be directly disabled, so this method provides a solution.
*/
function resizeThrottler() {
window.resizeTo(size[0], size[1]);
}
window.addEventListener('resize', resizeThrottler, false);
Message Communication
Chrome extension resources are divided into three types: popup/content/background. Content scripts can communicate directly with web pages, so if popup needs to send messages to a webpage, it can send to content script, which then forwards the message to the webpage.
In content.js, receive messages using chrome.runtime.onMessage, and send messages to webpages using window.postMessage
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener(
(message, sender, sendResponse) => {
window.postMessage(message, '*');
return true;
},
);
Popup sends messages to content.js using chrome.tabs.sendMessage
chrome.tabs.sendMessage(tabId, message);
Additionally, Chrome can receive messages sent from web pages
Web pages send messages to extensions using chrome.runtime.sendMessage
var hasExtension = false;
const extensionId = 'bmkmhpkgcbigmdepppdpdhlifcgoibph';
chrome.runtime.sendMessage(extensionId, {operation: "installCheck"},
function (reply) {
if (reply && reply.data.version) {
hasExtension = true;
} else {
hasExtension = false;
}
});
Extension background receives messages using chrome.runtime.onMessageExternal.addListener
chrome.runtime.onMessageExternal.addListener((request, sender, sendResponse) => {
})
chrome.runtime Returns undefined
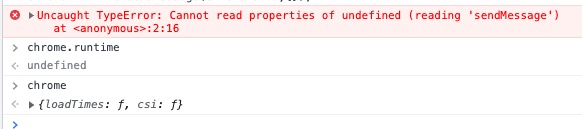
When web pages send messages to extensions, ensure that externally_connectable in settings can match the webpage, otherwise chrome.runtime returns undefined
Example configuration:
"externally_connectable": {
"matches": [
"https://*.19991421.cn",
"http://127.0.0.1/*"
]
}
http://*/*,https://*/*cannot match IP addresses and localhost domains, so internal network URLs need separate configuration.- Port numbers don’t need consideration, they are wildcard by default.
- It’s not recommended to configure
http://*/*,https://*/*- although it works, browser extensions will show errorWildcard domain patterns such as "http://*/*" are not allowed
Popup Maximum Width and Height
Maximum width 800px, maximum height 600px. HTML tag level will enforce this size. If child tags exceed these dimensions, scrolling will be displayed.
Recommended dimensions: 600px height, 357px width
DevTools failed to load source map: Could not load content
Chrome extensions only support inline source maps, so you need to modify build tool configuration - don’t use separate source map configuration, use something like inline-source-map
Hot Reload
Extensions are different from regular web development, so hot reload configuration is different. Recommended to use the ExtensionReloader plugin with the following configuration:
new ExtensionReloader({
port: 9090, // Which port use to create the server
reloadPage: true, // Force the reload of the page also
entries: {
popup: "popup", background: "eventPage", contentScript: "contentScript"
}
})
Note: The property values in entries correspond to the entry names configured in webpack’s entry section, not physical file path names.
Extension Template - Practice
All these configurations can be viewed in the template:
https://github.com/alanhe421/chrome-extension-react-typescript-boilerplate
Extension Updates
- Official Store Distribution
In this method, extensions will
auto-update. The auto-update frequency might be around 5 hours. - Self-hosted Distribution Packages
- update_url field, but in this method, what’s hosted is the CRX signed distribution package. Unsigned packages won’t work.
- Update packages must be CRX files
{
"name": "My extension",
...
"update_url": "http://myhost.com/mytestextension/updates.xml",
...
}
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<gupdate xmlns='http://www.google.com/update2/response' protocol='2.0'>
<app appid='aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa'>
<updatecheck codebase='http://myhost.com/mytestextension/mte_v2.crx' version='2.0' />
</app>
</gupdate>
- Development Packages Implement custom check logic, such as prompting when popup opens or timer checks, push notifications when updates are available. Users download new packages for overwrite. After overwriting, restart browser or manually click update in extension page.
manifest.json Configuration Changes
After modification, browser restart is required to take effect
Modifying Page Windows
Final Thoughts
Chrome extension development comes with its own set of challenges and best practices. Understanding message communication patterns, proper configuration of externally_connectable domains, and handling popup limitations are crucial for successful extension development. The hot reload setup with ExtensionReloader significantly improves development workflow, while proper source map configuration ensures smooth debugging. Always test extension updates thoroughly and consider both store distribution and self-hosted options based on your deployment needs.

