Recently, an open source project needed to implement a web3.js library, so I researched the leading web3.js library - ethers.js.
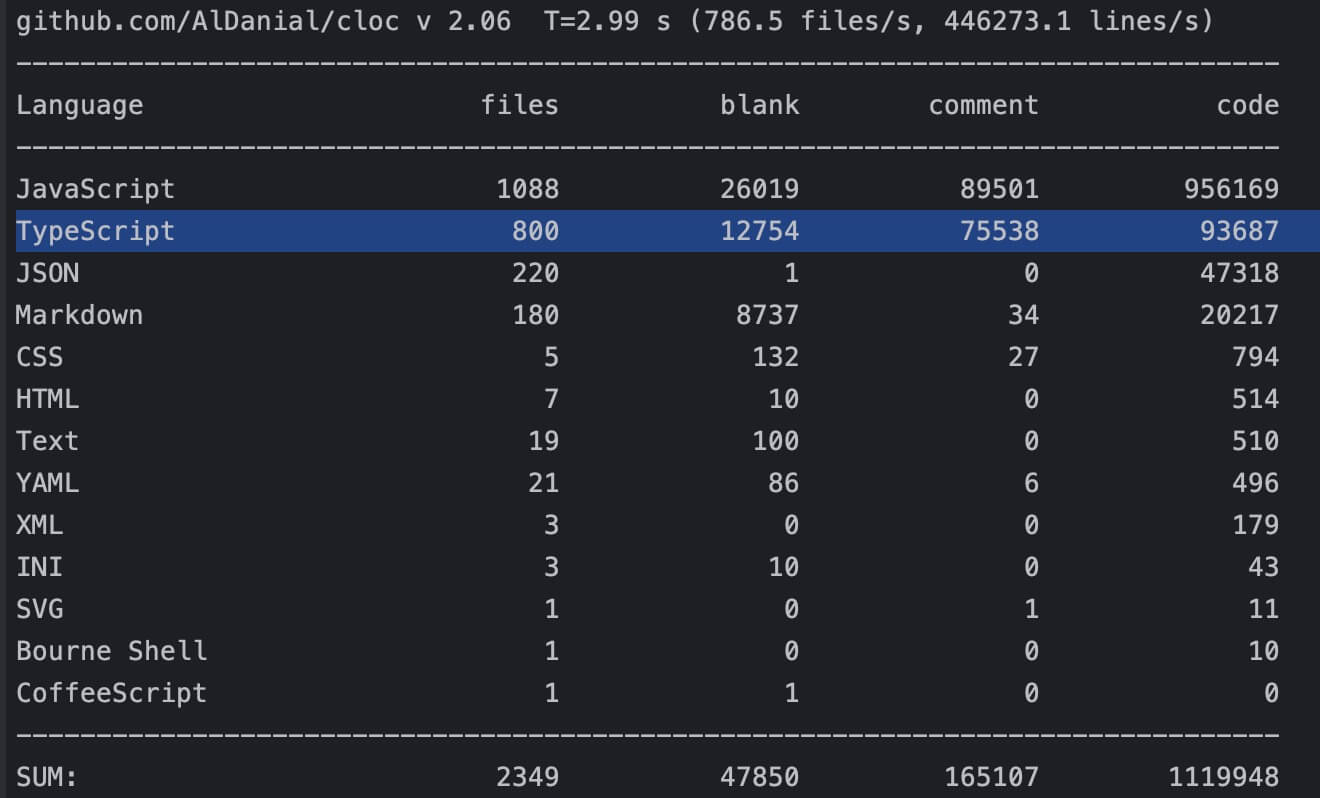
Code Size
The source code is written in TypeScript, with actual code size around 90k lines.
Cross-Platform Support
ethers.js outputs both ES and CJS compliant code, therefore supporting both Browser and server-side Node.js.
- lib.commonjs
- lib.esm
Features
- Wallet management (Wallet)
- Ethereum node interaction (Provider)
- Smart contract interaction (Contract)
- Transaction processing
- Utility and helper functions
- Support for multiple Ethereum-compatible chains
Architecture
ethers.js is a modular library that includes the following modules:
1. ABI Module (src.ts/abi)
Responsibility: Handle Ethereum Application Binary Interface (ABI)
abi-coder.ts:AbiCoderclass, responsible for ABI encoding/decodinginterface.ts:Interfaceclass, parse contract ABI, handle function calls and eventsfragments.ts: Define ABI fragment types (functions, events, errors, etc.)coders/: Various data type encoders/decoders
2. Address Module (src.ts/address)
Responsibility: Handle Ethereum address-related operations
- Address validation and formatting
- Contract address calculation (CREATE, CREATE2)
- ICAP address format support
4. Contract Module (src.ts/contract)
Responsibility: Smart contract interaction
contract.ts:Contractclass, provides contract method call interfacefactory.ts: Contract deployment factorywrappers.ts: Event log and transaction receipt wrapper classes
5. Cryptography Module (src.ts/crypto)
Responsibility: Cryptographic primitives and key management
signing-key.ts:SigningKeyclass, elliptic curve key operationssignature.ts: Digital signature processingkeccak.ts,sha2.tsetc.: Hash functionsscrypt.ts,pbkdf2.ts: Key derivation functions
6. Hash Module (src.ts/hash)
Responsibility: Various hashing and encoding operations
id.ts: String to hash conversionmessage.ts: Message signing and verificationtyped-data.ts: EIP-712 typed data signingnamehash.ts: ENS domain name hashing
7. Provider Module (src.ts/providers)
Responsibility: Blockchain network connection and data retrieval
abstract-provider.ts:AbstractProviderbase classprovider-jsonrpc.ts: JSON-RPC provider- Various third-party blockchain node service providers (Infura, Alchemy, etc.)
8. Transaction Module (src.ts/transaction)
Responsibility: Transaction creation, signing, and serialization
transaction.ts:Transactionclassaddress.ts: Address-related utility functions
9. Utilities Module (src.ts/utils)
Responsibility: Common utility functions
data.ts: Byte data processingerrors.ts: Error handlingfetch.ts: HTTP request wrappermaths.ts: Mathematical operationsutf8.ts: UTF-8 encoding/decoding
10. Wallet Module (src.ts/wallet)
Responsibility: Wallet management and key storage
wallet.ts:Walletclasshdwallet.ts: HD wallet implementationjson-keystore.ts: Keystore format supportmnemonic.ts: Mnemonic phrase processing
11. Wordlists Module (src.ts/wordlists)
Responsibility: Mnemonic wordlists
- Support for multilingual mnemonics
This modular design gives ethers.js clear separation of concerns, with each module focusing on specific functional areas, making it easy to maintain and extend.
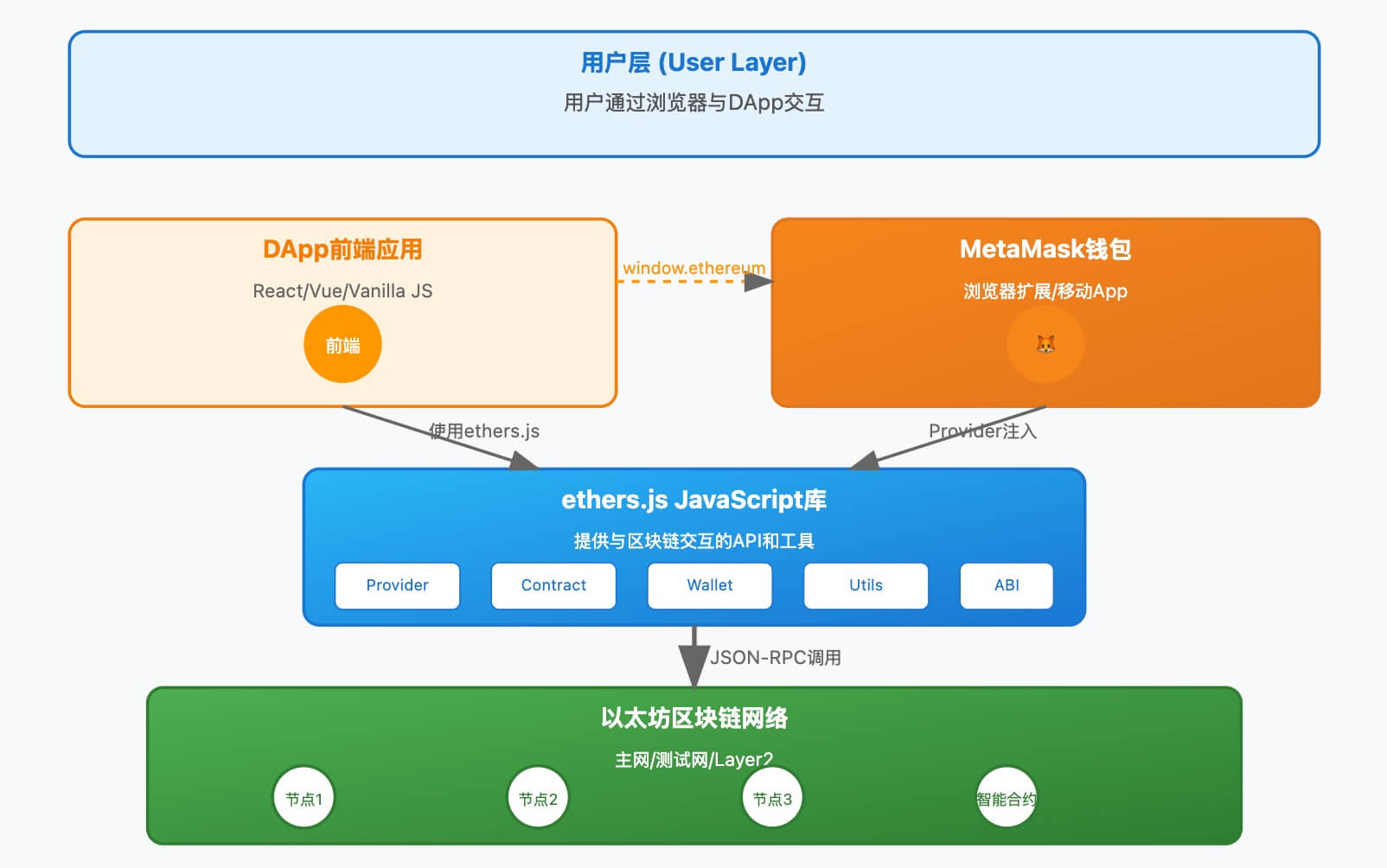
Relationship between ethers.js and MetaMask wallet
- Standardized interfaces: Both follow Ethereum standards like EIP-1193
- Separation of responsibilities:
- MetaMask: Private key management, user authorization, transaction signing
- ethers.js: Data formatting, ABI encoding/decoding, network communication
- Interchangeability: ethers.js can also work with other wallets (like WalletConnect)
MetaMask provides low-level primitive interfaces without any abstraction. While ethers.js provides higher-level abstractions and wrappers, making it more convenient for developers to interact with the Ethereum network.
Additional Concept Introduction
Smart Contracts
This name is indeed somewhat exaggerated, but it emphasizes several key characteristics:
- Automated execution
- Reduced human intervention
- Transparent and verifiable
- Reduced trust costs

