Due to work needs, I have used many terminals, such as iTerm2, Warp, Tabby, Hyper, etc.
Recently, I researched Wave Terminal and found some highlights, so I’ll introduce it here.

Platform
Wave is a local terminal, not web-based, currently supporting.
- Mac (M series also supported)
- Linux
- Windows WSL (Windows is also supported!)
For the Mac version, it’s about 224MB, which is acceptable.
Free and Open Source
Wave is an open-source and free terminal. It has similarities with Warp, such as block mode display, and is therefore also known as an open-source free Warp alternative.
Usage
Here’s how to use it. First, Wave doesn’t require a login, which is a 👍 point.
Connection
To log in to a remote machine, first create a connection.
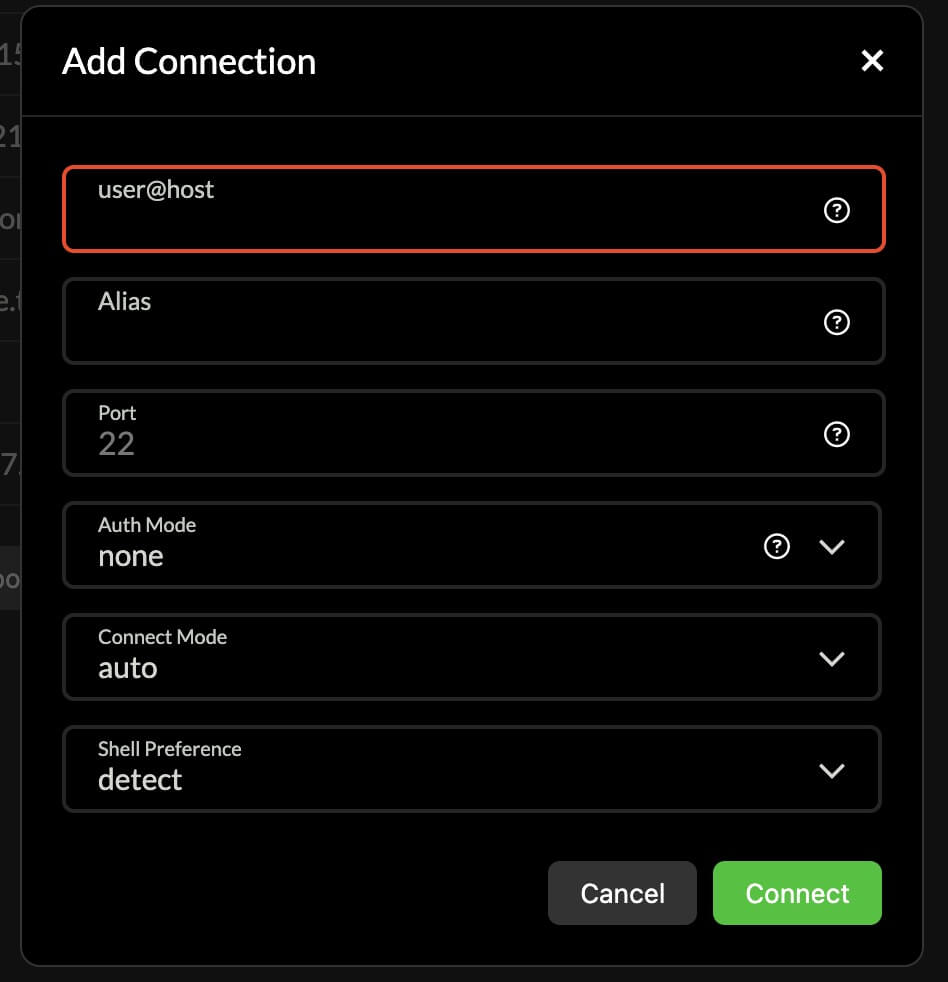
After creating, you can try to connect. If prompted to install remote scripts, click install, and once the connection is successful, you’re good to go.
Regarding connection configuration, the path to delete connection configurations is too cumbersome. Currently, you need to: select connection - delete - confirm deletion.
Workspace
In Wave, click on a workspace, then click Create New Tab, and choose the terminal connection to log in to the target machine. You can also customize the theme color of the session tab.
Workspace here is a form of session grouping. In practice, it can be divided into production/development/testing, etc., to avoid operational errors.
Command History
Wave records all commands executed in the terminal, including the command content, terminal connection, execution time, and more.
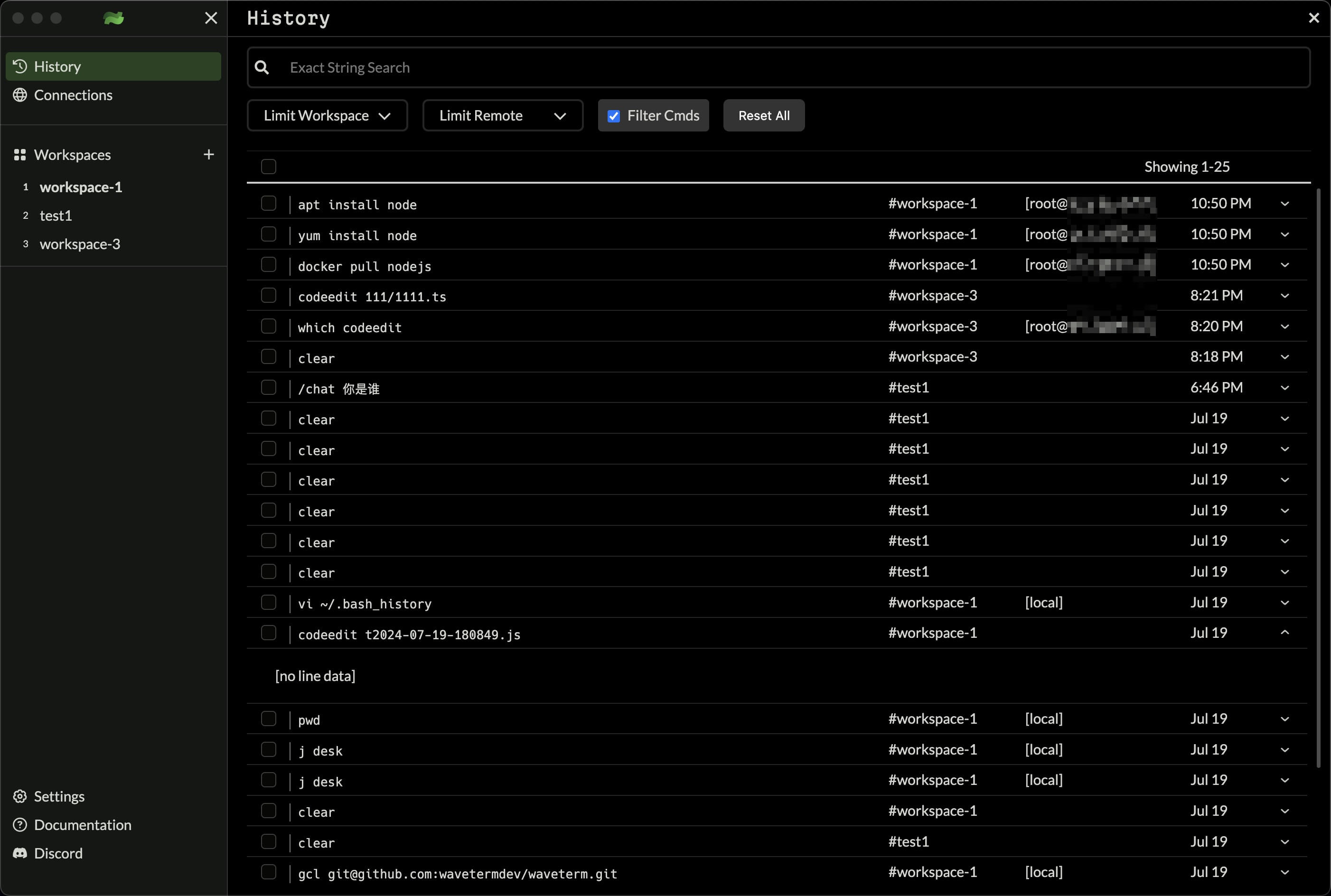
In addition to searching commands on the history page, you can also summon history reminders in actual terminal sessions with hotkeys for quick access.
The history is recorded in the local App database at $HOME/.waveterm/waveterm.db.
Commands in the history can be summoned and executed in any terminal session. You can choose commands from the history of the current machine or any command from across machines.
File Edit
Wave is weak in file-related operations. The only support is to input
codeedit filenamein the terminal to invoke file editing. You can set it to split-screen or block display mode.It does not support the
lrzszcommand for file upload/download, nor does it provide visual file management.

Others
The above are the core functions of Wave. Besides, Wave also provides some common features, such as AI and command completion.
Wave AI supports local AI models and cloud models (only supports OpenAI).
Usage:
- Right-side AI chat entrance
/chatcommand in terminal sessions- AI icon in command blocks
Regarding command completion, I find it quite useless at the moment, so I won’t introduce it.
OK, that’s all for Wave’s basic functions. Now for my personal view.
Advantages and disadvantages
disadvantages
As stated in the Wave open-source project’s issues, there are many problems in actual use, such as ineffective connection configuration deletion, ineffective configuration editing, and failure to install remote shell on remote machines, etc. You will encounter many issues in actual use. However, since the Wave open-source project started on Jun 5, 2022, we need to give it more time to develop. Its version number is not yet v1.0. Since it’s an open-source project, you can contribute as well, be it through issues or PRs.
Advantages
- The workspace organization is very innovative.
- The terminal supports input commands to operate features, such as
/chatfor AI Q&A, and/codeeditfor file editing.
At the end
Wave is still very immature. For users who frequently use terminals, I do not recommend using them because the issues are so many that they can hinder usage.
For infrequent users who can tolerate the issues, you can use it. After all, it is an open-source free terminal with Warp’s block display feature.

